Hallo Friends cellphone prices and specifications, In the article that you are reading this time with the title Per-App Language Preferences - Part 1, we have prepared this article well for you to read and take the information in it. hopefully the contents of the post Article Android Developers Blog, Article IFTTT, what we write you can understand. all right, have a nice reading..
Posted by Neelansh Sahai Android Developer Relations Engineer (on Twitter and LinkedIn) What if you have a set of users who are quite fluent in English, Hindi, and Spanish, and they have a news app on their phones and prefer to read the news in Hindi? For their texting app, they prefer Spanish as they have some friends and family who they text with in Spanish. But for ease of access, they still prefer their device to be in English. Now there are many such use-cases where the users might want their app languages to be different from their system language. Interesting!
What if you have a set of users who are quite fluent in English, Hindi, and Spanish, and they have a news app on their phones and prefer to read the news in Hindi? For their texting app, they prefer Spanish as they have some friends and family who they text with in Spanish. But for ease of access, they still prefer their device to be in English. Now there are many such use-cases where the users might want their app languages to be different from their system language. Interesting!
 |
Build for your multilingual users
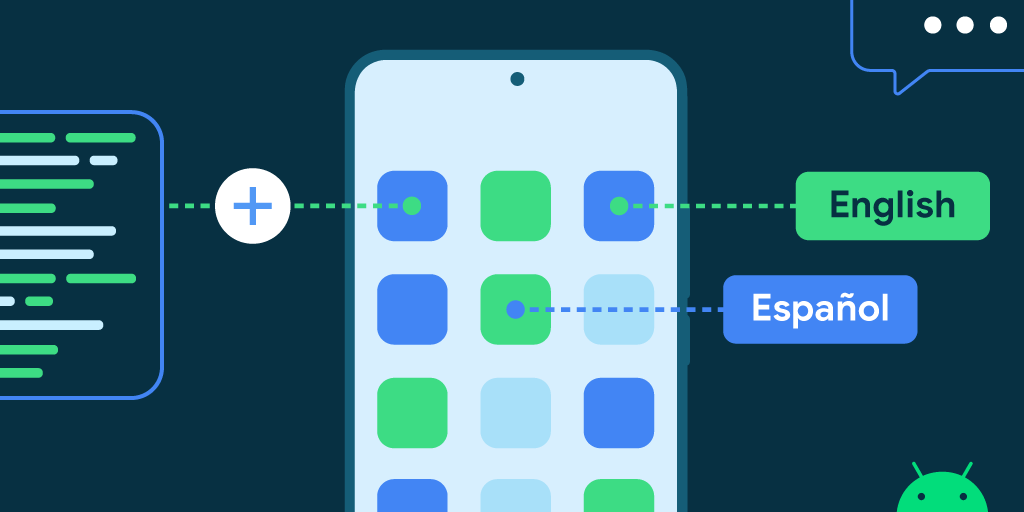
This blog focuses on how to integrate the Per-App Language Preferences API in your app to provide your users the flexibility to choose different languages for different apps.
1. Users can change the language settings from system settings by selecting:
Settings → System → Languages & Input → App Languages → [Select the desired App] → [Select the desired Language]
How to integrate this feature in your app?
There are 5 steps that need to be followed while working on the Per-App Language Preferences feature, listed here →
1. Create locale_config.xml file
Create a new file in values/xml/ directory and name it as locale_config.xml. This file should contain a list of all the locales that are supported by the app. The list element should be a string containing a locale tag.
locale_config.xml
2. Add the locale_config in the AndroidManifest.xml
Specify this locale_config.xml file in the app’s AndroidManifest.xml
AndroidManifest.xml
After steps 1 & 2, your users will be able to discover and set their language preference for your app from system settings on devices running Android 13 or higher. In case your users are on devices running on versions lower than Android 13, you can provide an in-app language picker. Optionally, you can also include the same language picker in your app for devices running Android 13 or higher. When your app includes an in-app language picker, it's important for the user's preferences to be in sync between the system and the app. This is where the AndroidX APIs come into the picture. Read on to learn how to create an in-app language picker.
3. Add the libraries
Steps 3, 4, & 5 above demonstrate the minimum components needed to create an in-app language picker.
And with this, your app can now support locale switching.
Additional things to take care of while migrating to the API
In this case, the system won’t be aware of the user’s preferences for the app language and thus it will map the app to the default system language. To avoid this, developers need to add some one-time migration logic so that their users don’t have to set the language again when they update the app.
What flexibility does the feature provide to the users and developers?
Here are a few things that might prove to be beneficial for you users.
- All devices running Android 13 or higher will have a common place for users to discover and change the language of their apps.
- Although the system settings are limited to the devices running Android 13 or higher, the AndroidX APIs are backwards compatible. Thus, there is no requirement to add OS Version checks in your code while building for your multilingual users.
- Developers do not need to handle configuration changes separately or worry about storing the user's selected language every time. The API handles configuration changes and stores the language preferences for you.
- Works with other Android features like Backup and restore. If a user switches to a new device and restores the previously backed up data, your app will retain the user’s last preferred language, thus providing your users with a better and more seamless experience.
Recap
With that, most parts of the feature are covered. So let’s have a quick recap on what we discussed in today’s read.
- A quick read on what Per-App Language Preferences offer to multilingual users and app developers.
- What end users will see on their devices.
- How to migrate your app to the Per-App Language Preferences APIs.
- A few things that need to be taken care of while migrating to the APIs to ensure a better user experience.
- Lastly, the benefits that end users and developers can leverage from this feature.
References
from Android Developers Blog https://ift.tt/GKA1xMw
via IFTTT
Thus the article Per-App Language Preferences - Part 1
You are now reading the article Per-App Language Preferences - Part 1 By address link https://cellphone-prices-and-specifications.blogspot.com/2022/11/per-app-language-preferences-part-1.html

![A cellphone screen demonstrating finding the language settings from system settings by selecting Settings → System → Languages & Input → App Languages → [Select the desired App] → [Select the desired Language]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEigMMkDrk24GFhwQYTFL3SOe7BtcvUXhnudcyYkJE4um0woEr2aRZ78LqcP8_UaqoSJliwQmoBllEw44RwSYuPTaG372Oyorri8Q_qkaapDOrzkU6nR_kWh9pQTx6Jj6Tqmjb4VwqiPtn43bZsOoAQyQ1RZ9kLnhbEScICv-ApjTaPNS7Gd3L4HxJZu/s1600/image1.gif)






0 Komentar untuk "Per-App Language Preferences - Part 1"